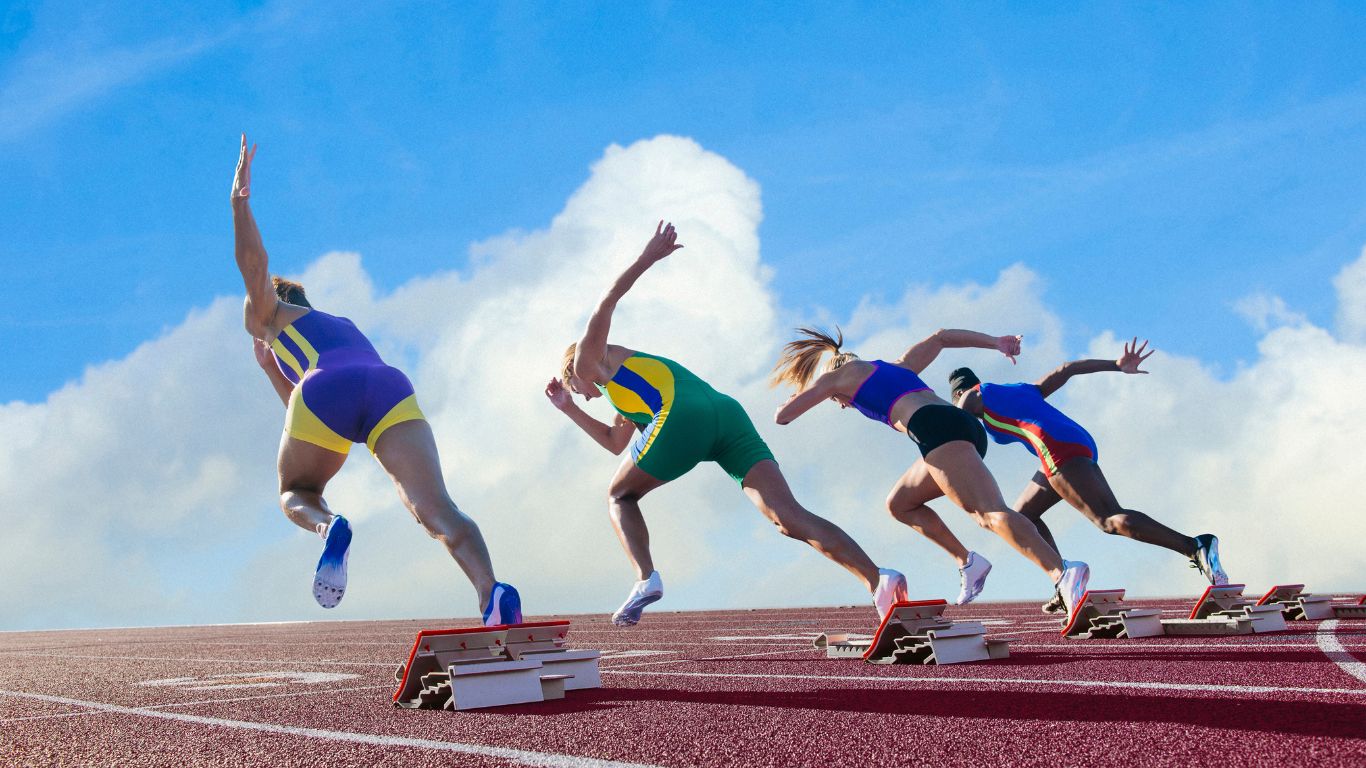
Track and Field, known universally as athletics, is one of the oldest forms of organized sport that tests its athletes’ speed, strength, agility, endurance, and skill. It has a rich history deeply rooted in human civilization, developed from primal human activities of running, jumping, and throwing.
A Brief History
The origins of track and Field can be traced back thousands of years. Cave paintings illustrate early instances of these physical contests, supporting that these activities have always been intrinsic to human nature.
Ancient Foundations

In antiquity, the Olympic Games of Greece forged the framework of competitive track and Field as we know it today. The games began in 776 BC and featured foot races, long jumps, discus throws, and other challenges. These early contests tested physical prowess and were integral to religious festivities.
Modern Era
Fast forward to the modern age; track and Field experienced a revival in 19th-century England. The Amateur Athletic Club, established in 1866, laid the groundwork for standardizing the sport. Following this, the inaugural modern Olympic Games in 1896 in Athens marked the global beginning of organized track and field events that continued to expand and evolve.
Main Events
The sport encompasses a variety of events that fall under two categories: track events and field events.
Track Events
- Sprints: Fast-paced races such as the 100m, 200m, and 400m.
- Middle-Distance and Long-Distance Running: Ranging from 800m to marathons.
- Hurdles: Races such as the 110m (men) and 100m (women) where athletes clear barriers.
- Relays: Team races, including the 4x100m and 4x400m events.
Field Events
- Jumping: The long jump, high jump, triple jump, and pole vault.
- Throwing: Including the shot put, discus, javelin, and hammer throw.
- Combined Events: The decathlon (men) and heptathlon (women) test versatility across multiple disciplines.
Training Techniques

Athletes in track and Field engage in specialized training to hone their skills and maximize performance.
- Interval Training: Vital for improving speed and cardiovascular endurance.
- Plyometric Exercises: Designed to develop explosive power, which is crucial for jumping and sprint events.
- Weight Training: Enhances strength and is foundational for all track and field athletes.
- Technique Drills: Event-specific exercises for perfecting form.
- Hill Training: Builds leg strength and endurance.
- Flexibility Training: Essential for maintaining a healthy range of motion.
- Endurance Runs: Increases aerobic capacity, particularly beneficial for distance events.
- Recovery and Regeneration: Practices that support healing to maintain peak physical condition.
Track and Field continues to captivate audiences worldwide through its diverse range of events and rich history. It remains a testament to human physical potential and competitive spirit.