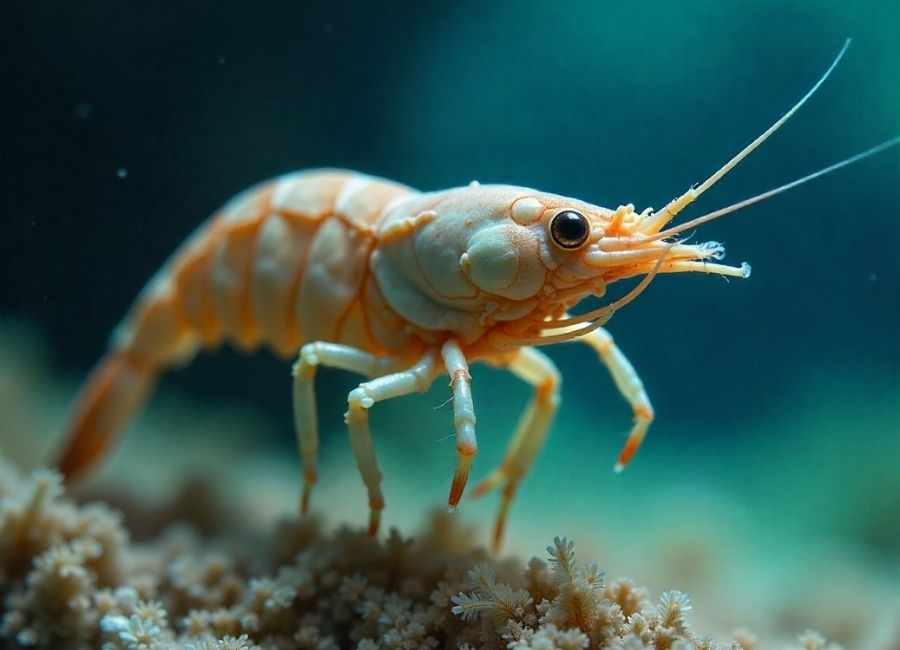
Shrimp may look small and fragile, but they are actually a key part of aquatic food webs. Many animals, from little fish to huge whales, rely on shrimp for food. Learning about what eats shrimp helps us see how marine life is connected and why balance in the ocean matters.
If you love marine biology, keep an aquarium, or are just curious about the ocean, this guide will show you the many animals that rely on shrimp to survive. We’ll look at their predators in different habitats, how shrimp protect themselves, and why they matter so much in the food chain.
Natural Predators of Shrimp in the Ocean
Shrimp face threats from predators at every level of the marine food chain. Their abundance and nutritional value make them an attractive meal for numerous ocean dwellers.
Large Fish Species
Many commercial fish species rely heavily on shrimp as a primary food source. Tuna, cod, haliMany fish that people catch for food depend on shrimp as a main part of their diet. Tuna, cod, halibut, and snapper all hunt shrimp in open water and near the sea floor. Some fish chase shrimp quickly, while others hide near rocks or coral and wait to surprise them. They lie on the ocean floor and wait for unsuspecting shrimp to pass within striking distance.
Sharks and Rays
While sharks are often associated with hunting larger prey, many species include shrimp in their diet. People usually think of sharks hunting big animals, but many sharks also eat shrimp. Smaller sharks and young sharks often feed on shrimp. For example, nurse sharks use strong suction to pull shrimp out of cracks in coral reefs. seafloor before consuming them. Their ke Rays also like to eat shrimp. Stingrays press their flat bodies against the seafloor to trap shrimp before eating them. They have a strong sense of smell that helps them find shrimp hidden in sand or mud. Seals and sea lions will eat shrimp when available, though they typically prefer larger fish. These agile swimmers can dive to significant depths to access shrimp populations on the ocean floor.
Baleen whales, including humpback and gray whales, consume enormous quantities of krill (a shrimp-like crustacean) during feeding seasons. While krill are technically different from true shrimp, they occupy a similar ecological niche and are targeted by many of the same predators.
Coastal and Estuarine Predators
Coastal areas and estuaries, where rivers meet the sea, are special places for shrimp. Many kinds of shrimp and their predators live in these mixed water habitats.

Seabirds
Birds are a big danger to shrimp in shallow coastal waters. Herons, egrets, and pelicans are skilled at catching shrimp. They walk through shallow water or dive from above to grab shrimp quickly and accurately.
Seagulls and terns also eat shrimp, especially at low tide when shrimp get stuck in tidal pools. These birds often follow fishing boats, hoping to find shrimp that are thrown back into the water.
Crabs and Lobsters
Ironically, some of the shrimp’s closest relatives are Interestingly, some of shrimp’s closest relatives are also their hunters. Crabs and lobsters look for shrimp in rocky areas and coral reefs. Their strong claws help them catch and break open shrimp shells easily. Shrimp have varied diets. These crustaceans often compete with shrimp for the same food sources, adding another layer to their predator-prey relationship.
Octopuses and Squid
Cephalopods, like octopuses, are smart hunters with clever ways to catch shrimp. Octopuses use their arms to search for cracks and coral where shrimp hide. They can change their color and texture to sneak up on shrimp without being seen. quid hunt in groups, using coordinated movements to herd shrimp into concentrated areas before attacking. Their speed and agility make them particularly effective predators in open water environments.
Freshwater Shrimp Predators
Freshwater shrimp have different predators than those in the ocean, but many of the ways they are hunted are similar.

Freshwater Fish
Bass, catfish, and trout are among the most common freshwater predators of shrimp. In rivers and lakes where freshwater shrimp populations thrive, these fish have adapted their feeding behaviors to exploit this abundant food source.
Cichlids and other ornamental fish kept in aquariums wilCichlids and other pet fish in aquariums may also eat small shrimp. People who keep aquariums need to think about which fish can live safely with shrimp, as they all prey on freshwater shrimp. These predators are particularly effective in shallow streams and ponds where shrimp populations are concentrated. Turtles use their sharp beaks to crush shrimp shells, while frogs rely on their sticky tongues to capture fast-moving prey.
Water snakes also hunt freshwater shrimp, though they Water snakes also hunt freshwater shrimp, but they usually go after bigger prey if they can. Young or smaller snakes are more likely to eat shrimp. The meal for so many predators, shrimp have evolved several defense mechanisms to improve their survival odds.
Speed and Agility
Shrimp can quickly shoot backward by snapping their tails, a move called a “tail flip.” This helps them escape from predators fast. Shrimp species have developed coloration that helps them blend into their surroundings. Clear or translucent bodies make some shrimp nearly invisible in open water, while others have patterns that mimic the coral or rocks they live among.
Nocturnal Behavior
Shrimp are primarily nocturnal creatures. Shrimp mostly come out at night to feed, staying hidden during the day. This helps them avoid daytime predators, but it means they have to watch out for animals that hunt at night. form large schools or congregate in areas with complex structures like coral reefs. These group behaviors make it harder for predators to target individual shrimp and provide more eyes to watch for approaching danger.
The Ecological Importance of Shrimp
Shrimp are an important link in the food chain. They eat things like algae and plankton and turn them into protein that bigger animals can use. If there weren’t enough shrimp, many fish that people catch for food would have trouble finding enough to eat.
Shrimp also help move nutrients around in the ocean. As they eat, they break down old plant and animal material and spread nutrients through the water. This helps tiny plants like phytoplankton grow, which are the start of the food web.
Commercial fishing industries depend heavily on understanding predator-prey relationships. Fishing businesses need to understand how shrimp fit into the food web. If too many shrimp are caught, it can upset the balance in the ocean and affect many other animals, from small reef fish to big ocean fish. Commercial shrimp fishing is a multi-billion-dollar industry worldwide. While this provides food and economic benefits, it also creates challenges for maintaining sustainable shrimp populations.
Aquaculture has emerged as an alternative to wild-caught shrimp, but it brings its own set of problems. Farming shrimp is now common instead of catching them in the wild, but this also causes problems. Shrimp farms can harm coastal areas and sometimes spread diseases to wild shrimp. Climate change and changes in ocean chemistry are new threats to shrimp. Warmer water and different water conditions can make it harder for shrimp to survive and reproduce, which can upset the food chain. toward protecting these vital creatures and the ecosystems they support. Conservation efforts must consider the complex web of relationships that connect shrimp to countless other species.
Setting up protected areas in the ocean can help keep shrimp habitats safe and keep predator numbers balanced. Using better fishing methods and limits can also help shrimp populations grow back.
If you keep an aquarium, being a responsible pet owner means learning which animals can live together peacefully. With the right planning and tank mates, many types of freshwater shrimp can do well in community tanks.
Next time you encounter shriThe next time you see shrimp, whether in the ocean, at the store, or in an aquarium, take a moment to think about how important they are for many ecosystems. Even though many animals eat them, shrimp play a big part in keeping the aquatic food web healthy.










